Microsoft Autorecovery Folder Is Empty
- Microsoft Autorecovery Folder Is Empty
- Microsoft Auto Recovery Folder Is Empty Free
- Microsoft Auto Recovery Folder Is Empty Download
'Restore' the AutoRecover file (it will ask what folder you want to restore the file to) Open the AutoRecover file, and re-save your recovered work. Maybe you can try uFlysoft Data Recovery for Mac, it can recover empty trash on Mac only in three steps: Step 1. Launch the software to scan the device where your files deleted. Step 3: Change the link to the damaged document. Right-click the linked text in the document, point to Linked Document Object, and then select Links. In the Links dialog box, select the file name of the linked document, and then select Change Source. In the Change Source dialog box, select the document that you cannot open, and then select Open.
Find lost files when autosave fails in Microsoft Word
When writing, nothing breaks Csikszentmihalyi-style flow more quickly or completely than losing work to a BSOD or unexpected power outage. Fortunately, modern versions of Microsoft Word contain features to minimize lost work when crashes happen. When opening Word after a failure, you may have seen the Document Recovery window appear, offering to open the last autosaved version of your document.
Document Recovery has saved me countless hours of lost work over the years, but sometimes Word doesn't realize that a crash has occurred, or something else prevents Document Recovery from opening automatically. Thankfully, if autosave is active (and it is, unless you manually turned it off), your work is probably not lost. Here's how to retrieve it.
Step 1: Locate the Word autorecover file location
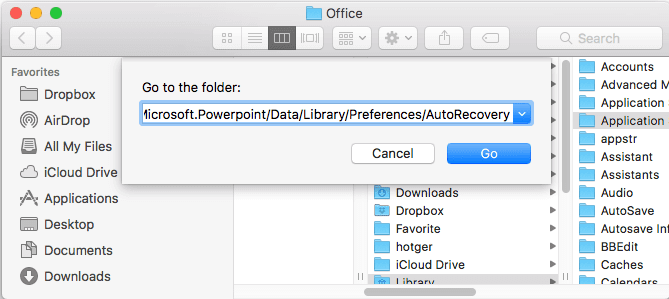
In Office 2010, click on File | Options to bring up the Word Options dialog box. (In Office 2007, click on the Office Orb, then Options.) In the left-hand column, select Save. In the Save options section, highlight the path in the Autorecover file location box and press CTRL+C to copy the path.

Step 2: Navigate to the autorecover file location from within Word


Open Microsoft Word, and select File | Open. Place your cursor in the File name box and press CTRL+V to paste the path to the autorecover file location. Press Enter to open the directory.
Step 3: Open the appropriate autorecovery file
In the file type dropdown list, select All Files (*.*). At this point, you should see one (or more) files with the extension .asd. These are the Word autorecovery files. If the document was new and never saved, the filename will be something like 'Autorecovery save of Document1.asd.' If the document was already manually saved, but you lost intervening work between saves, it will have the name of the saved document (e.g., 'Autorecovery save of Rob's Grocery List.asd').
Microsoft Autorecovery Folder Is Empty
Select the appropriate .asd file and click Open. In some cases, the .asd file may not even have an intelligible filename (e.g., '~prj383.asd'). If no file in the directory has the expected file name, open each .asd file until you find the one that contains your missing work.
Microsoft Auto Recovery Folder Is Empty Free
Voila! Your document is back, and at most you've only lost the last 10 minutes of work.
Additional Tip:
In the Save options section (from Step 2 above), reduce the duration between autosaves. You can make the duration between autosaves as small as 1 minute, but when working on long and complex documents (e.g., a dissertation or scholarly article) sometimes the autosave process itself can disrupt your flow, especially on older, slower computers. I recommend setting the Save autorecover information every value to 2 minutes. This way, when future incidents occur, the most you can possibly lose is 2 minutes of work. When crashes happen, 2 minutes of re-writing will be sub-optimal, but will hopefully fail to break your creative flow. Csikszentmihalyi would approve.